✏️ 반복자 패턴 Iterator Pattern
반복자 패턴 : 컬렉션의 구현 방법을 노출하지 않으면서 집합체 내의 모든 항목에 접근하는 방법을 제공함.
- 반복자 패턴을 사용하면 각 항목에 일일이 접근할 수 있게 해주는 기능을 집합체가 아닌 반복자 객체가 책임진다는 장점이 있다.
- 반복자 객체와 집합체의 기능이 분리되면 집합체 인터페이스와 구현이 간단해지고, 각자에게 중요한 일만 처리할 수 있게 된다.
- 컬렉션 객체 안에 들어있는 모든 항목에 접근하는 방식이 통일되어 있으면, 종류에 관계없이 모든 집합체에 사용할 수 있는 다형적인 코드를 만들 수 있다.
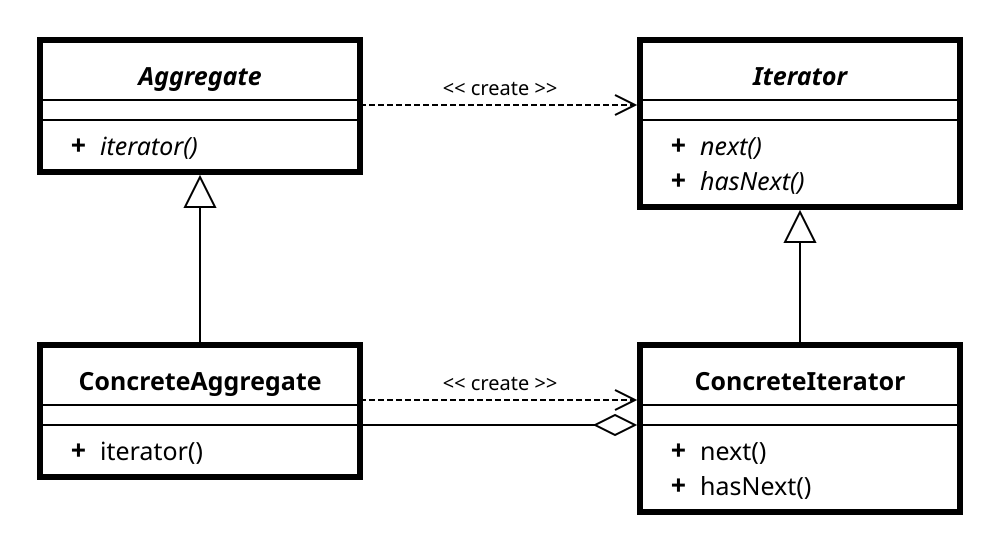
🔁 ArrayList와 array의 반복을 반복자 패턴으로 캡슐화하기
- 반복자 패턴은 Iterator 인터페이스에 의존한다.
hasNext(): 반복 작업을 적용할 대상이 더 있는지 확인할 수 있다.next(): 다음 객체를 리턴한다.
- 반복자를 사용하면, 그 안에 들어있는 모든 항목에 접근할 수 있게 하려고 여러 메소드를 외부에 노출시키지 않으면서도 컬렉션에 들어있는 모든 객체에 접근할 수 있다.
- 또한 반복자를 구현한 코드를 컬렉션 밖으로 끄집어낼 수 있어 캡슐화할 수 있다.
Iterator implement하여 구현하기
Iterator 인터페이스 정의
1
2
3
4
public interface Iterator {
boolean hasNext();
MenuItem next();
}
DinerMenu클래스에서 사용할 구상 Iterator 클래스 만들기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class DinerMenuIterator implements Iterator {
MenuItem[] items;
int position = 0;
public DinerMenuIterator(MenuItem[] items) {
this.items = items;
}
public MenuItem next() {
MenuItem menuItem = items[position];
position = position + 1;
return menuItem;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
if (position >= items.length || items[position] == null) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
DinerMenu 클래스에서 반복자를 사용하기
- DinerMenu에서는 메뉴를 배열에 담았다.
- PancakeHouseMenu에서는 메뉴를 ArrayList에 담았다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
public class DinerMenu { static final int MAX_ITEMS = 6; int numberOfItems = 0; MenuItem[] menuItems; // 생성자 // addItem 메소드 호출 public Iterator createIterator() { return new DinerMenuIterator(menuItems); } // 기타 메뉴 관련 메소드 }
종업원 코드에서는 반복자를 아래와 같이 적용할 것이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public class Waitress {
PancakeHouseMenu pancakeHouseMenu;
DinerMenu dinerMenu;
public Waitress(PancakeHouseMenu pancakeHouseMenu, DinerMenu dinerMenu) {
this.pancakeHouseMenu = pancakeHouseMenu;
this.dinerMenu = dinerMenu;
}
public void printMenu() {
Iterator pancakeIterator = pancakeHouseMenu.createIterator();
Iterator dinerIterator = dinerMenu.createIterator();
System.out.println("메뉴\n ----- \n 아침메뉴");
printMenu(pancakeIterator);
System.out.println("\n 점심메뉴");
printMenu(dinerIterator);
}
private void printMenu(Iterator iterator) {
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MenuItem menuItem = iterator.next();
System.out.print(menuItem.getName() + ", ");
System.out.print(menuItem.getPrice() + " -- ");
System.out.println(menuItem.getDescription());
}
}
}
- 반복자가 생겨서, Waitress 클래스가 실제로 구현된 구상 클래스로부터 분리되었다.
- Menu가 ArrayList인지, array인지는 신경 쓸 필요가 ㅇ벗다. Iterator를 받아서 컬랙션에 들어있는 모든 객체를 사용할 수만 있으면 된다.
java.util.Iterator 인터페이스를 적용해 개선하기
java.util.Iterator
1
2
3
4
5
public interface Iterator {
hasNext();
next();
remove();
}
ArrayList에는 반복자를 리턴하는 iterator()메소드가 있지만, 배열에는 반복자를 만드는 방법이 없으니, DinerMenu에는 반복자를 구현해야 한다.
PancakeHouseMenu에 적용하기
1
2
3
public Iterator<MenuItem> createIterator() {
return menuItems.iterator();
}
DinerMenu에 적용하기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
import java.util.Iterator;
public class DinerMenuIterator implements Iterator<MenuItem> {
MenuItem[] items;
int position = 0;
public DinerMenuIterator(MenuItem[] items) {
this.items = items;
}
public MenuItem next() {
//기타 코드
}
public boolean hasNext() {
//기타 코드
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("메뉴 항목은 지우면 안됩니다.");
}
}
Menu 인터페이스 통일하기
1
2
3
public interface Menu {
public Iterator<MenuItem> createIterator();
}
종업원 코드에 적용하기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Waitress {
Menu pancakeHouseMenu;
Menu dinerMenu;
public Waitress(Menu pancakeHouseMenu, Menu dinerMenu) {
this.pancakeHouseMenu = pancakeHouseMenu;
this.dinerMenu = dinerMenu;
}
public void printMenu() {
Iterator pancakeIterator = pancakeHouseMenu.createIterator();
Iterator dinerIterator = dinerMenu.createIterator();
System.out.println("메뉴\n ----- \n 아침메뉴");
printMenu(pancakeIterator);
System.out.println("\n 점심메뉴");
printMenu(dinerIterator);
}
private void printMenu(Iterator iterator) {
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MenuItem menuItem = iterator.next();
System.out.print(menuItem.getName() + ", ");
System.out.print(menuItem.getPrice() + " -- ");
System.out.println(menuItem.getDescription());
}
}
}
📒 단일 역할 원칙 Single Responsibility Principle
어떤 클래스가 바뀌는 이유는 하나뿐이어야 한다.
즉, 클래스는 단 핸개의 책임을 가져야 한다.
집합체에서 내부 컬렉션 관련 기능과 반복자용 메소드 관련 기능을 전부 구현한다면,
- 컬렉션이 어떤 이유로 바뀌게 되면 그 클래스도 바뀌어야 한다.
- 반복자 관련 기능이 바뀌었을 때도 클래스가 바뀌어야 한다.
어떤 클래스에서 맡고 있는 모든 역할은 나중에 코드 변화를 불러올 수 있다. 역할이 2개 이상 있으면 바뀔 수 있는 부분이 2개 이상이 된다.
응집도 cohension
한 클래스 또는 모듈이 특정 목적이나 역할을 얼마나 일관되게 지원하는지를 나타내는 척도.
- 응집도가 높다는 것: 서로 연관된 기능이 묶여있다는 것
- 응집도가 낮다는 것: 서로 상관 없는 기능들이 묶여있다는 것
SRP를 잘 지키는 클래스는 2개 이상의 역할을 맡고 있는 클래스에 비해 응집도가 높고, 관리하기 쉽다.
리팩토링 하기
- 새로운 메뉴와 서브메뉴를 추가할 수 잇는 트리 형태의 구조로 만들기
- 각 메뉴에 있는 모든 항목을 대상으로 특정 작업을 할 수 잇는 방법을 제공해야 한다.
- 더 유연한 방법으로 아이템을 대상으로 반복 작업을 수행할 수 있어야 한다.
✏️ 컴포지트 패턴 Composite Pattern
컴포지트 패턴 : 객체를 트리구조로 구성해서 부분-전체 계층구조를 구현한다. 컴포지트 패턴을 사용하면 클라이언트에서 개별 객체와 복합 객체를 똑같은 방법으로 다룰 수 있다.
- 객체의 구성과 개별 객체를 노드로 가지는 트리 형태의 객체 구조를 만들 수 있다.
- 복합 객체와 개별 객체를 대상으로 똑같은 작업을 적용할 수 있다. 복합 객체와 개별 객체를 구분할 필요가 거의 없어진다.
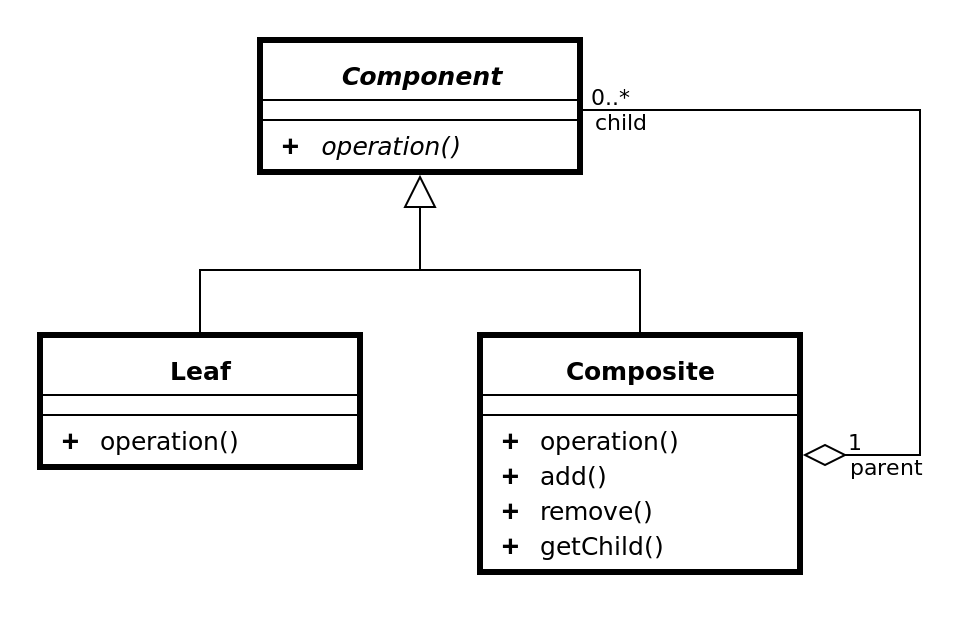
부분-전체 계층 구조 part-whole hierarchy
부분들이 계층을 이루고 있지만 모든 부분을 묶어서 전체로 다룰 수 있는 구조
- 메뉴, 서브메뉴, 서브의 서브 메뉴로 구성된 트리구조가 있다고 하면, 각각이 모두 복합 객체가 될 수 있다.
- 개별 객체도 메뉴라고 할 수 있다.
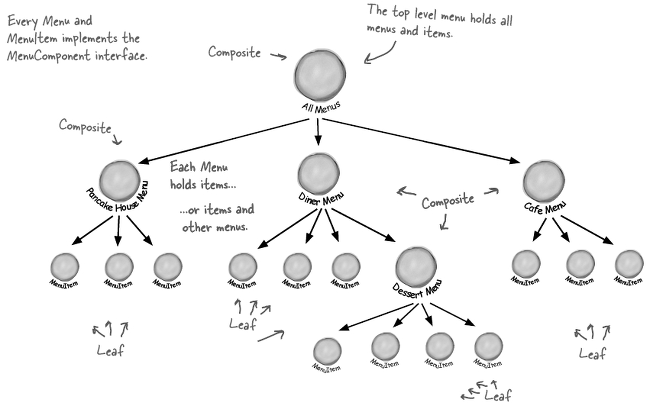
컴포지트 패턴을 메뉴에 적용하기
1. Component 인터페이스 만들기
Component는 메뉴와 메뉴 항목 모두에 적용되는 공통 인터페이스 역할을 한다.
인터페이스가 있어야만 메뉴와 메뉴 항목들을 똑같은 방법으로 처리할 수 있다.(= 같은 메소드를 호출할 수 있다)
MenuComponent 인터페이스
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public interface MenuComponent {
getName();
getDescription();
getPrice();
isVegetarian();
print();
add(MenuComponent);
remove(MenuComponent);
getChilde(int);
}
2. MenuComponent 구현하기
- 모든 구성 요소에
MenuComponet인터페이스를 구현해야만 한다. - 하지만 잎과 노드는 각각 역할이 다르기 때문에 모든 메소드에 알맞는 기본 메소드 구현은 불가능하다.
MenuItem에서는MenuItem에 쓰일만한 메소드만 오버라이드 하고, 나머지는 기본 구현을 그대로 사용한다.- getName()
- getDescription()
- getPrice()
- isvegetarian()
- print()
Menu에서는Menu에 쓰일만한 메소드만 오버라이드한다.- getName()
- getDescription()
- print()
- add(MenuComponent)
- remove(MenuComponent)
- getChild(int)
- 따라서 자기 역할에 맞지 않는 상황에는 예외를 던지는 코드를 기본 구현으로 한다. 자기 역할에 맞지 않는 메소드는 오버라이드 하지 않고 기본 구현을 그대로 사용할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
public abstract class MenuComponent {
public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOprationException();
}
public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOprationException();
}
public MenuComponent getChild(int i) {
throw new UnsupportedOprationException();
}
public void getName() {
throw new UnsupportedOprationException();
}
public void getDescription() {
throw new UnsupportedOprationException();
}
public void getPrice() {
throw new UnsupportedOprationException();
}
public void isVegetarian() {
throw new UnsupportedOprationException();
}
public void print() {
throw new UnsupportedOprationException();
}
}
3. MenuItem 구현하기
- 컴포지트 패턴 다이어그램에서 잎에 해당하는 클래스
- 복합 객체의 원소에 해당하는 행동을 구현해야한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public class MenuItem extends MenuComponents {
String name;
String description;
boolean vegetarian;
double price;
public MenuItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.vegeterian = vegetarian;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public boolean isVegeterian() {
return vegeterian;
}
public void print() {
System.out.print(" " + getName());
if (isVegetarian()) {
System.out.print("(v)");
}
System.out.println(", " + getPrice());
System.out.println(" ---- " + getDescription());
}
}
4. Menu 구현하기
- 복합객체 클래스다
- 복합객체 클래스에는
MenuItem, 다른Menu를 저장할 수 있다. - getPrice(), isVegeterian()은 메뉴에서 별 의미가 없으므로 구현하지 않는다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
public class Menu extends MenuComponents {
List<MenuComponent> menuComponents = new ArrayList<MenuComponent>();
String name;
String description;
public Menu(String name, String description) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
}
public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
menuComponents.add(menuComponent);
}
public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
menuComponents.remove(menuComponent);
}
public MenuComponent getChild(int i) {
return menuComponents.get(i);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void print() {
System.out.print(" " + getName());
System.out.println(", " + getDescription());
for (MenuComponent menuComponent : menuComponents) {
menuComponent.print();
}
}
}
5. Waitress에 적용하기
- 종업원 = 이 코드를 사용하는 클라이언트
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class Waitress {
MenuComponent allMenus;
public Waitress(MenuComponet allMenus) {
this.allMenus = allMenus;
}
public void printMenu() {
allMenus.print();
}
}
정리
- 컴포지트 패턴은 계층 구조를 관리하는 일과 메뉴 관련 작업을 처리한다.
- 컴포지트 패턴은 단일 역할 원칙을 깨는 대신 투명성을 확보하는 패턴이다.
- 투명성: 어떤 원소가 복합 객체인지 잎인지가 클라이언트에게 투명하게 보이는 것
- 두 종류의 기능이 모두 들어가서 안전성은 약간 떨어진다. 클라이언트가 어떤 원소를 대상으로 무의미하거나 부적절한 작업을 처리하려고 할 수도 있다.
- 아무일도 하지 않거나 null, false 등을 상황에 맞게 리턴하는 방법, 예외를 던지는 방법이 있다.
- 클라이언트에서 예외 상황을 적절히 처리할 준비를 하고 있어야 한다.
- 상황에 따라 디자인 원칙을 적절하게 사용해야한다.
reference
HeadFirst Design Pattern
